Evaluating Retrieval Augmented Generation Pipelines with LlamaIndex and TruLens
Recently RAG pipelines have emerged as most useful technique for building question-answering systems. By combining information retrieval and language generation, RAG pipelines can provide relevant and context-aware responses to user queries. However, evaluating the performance of these pipelines can be a challenging task, requiring a systematic approach to measure various aspects of the system's outputs.
In this blog, I will explore how to set up and evaluate RAG pipelines using LlamaIndex, a Python library for building and querying document indices, and TruLens, a tool for evaluating the performance of generative AI applications. We will start by building a basic RAG pipeline and then dive into advanced retrieval techniques, such as sentence window retrieval and auto-merging retrieval. Throughout the process, I'll use TruLens to define a set of metrics and benchmark the performance of each pipeline against a set of evaluation questions.
Data and Tools:
Data:
The ebook "How to Build a Career in AI" serves as the source of information.
Tools:
LlamaIndex: Used for building and querying document indices.
OpenAI:
Provides the GPT-3.5-turbo language model for text generation.
from llama_index.llms import OpenAI
llm = OpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0.1)
This code imports the OpenAI LLM from the llama_index.llms module and initializes an instance of it with the gpt-3.5-turbo model and a temperature of 0.1 (for less random output).
TruLens:
Evaluates the RAG pipeline's performance on various metrics.
Pipeline Stages:
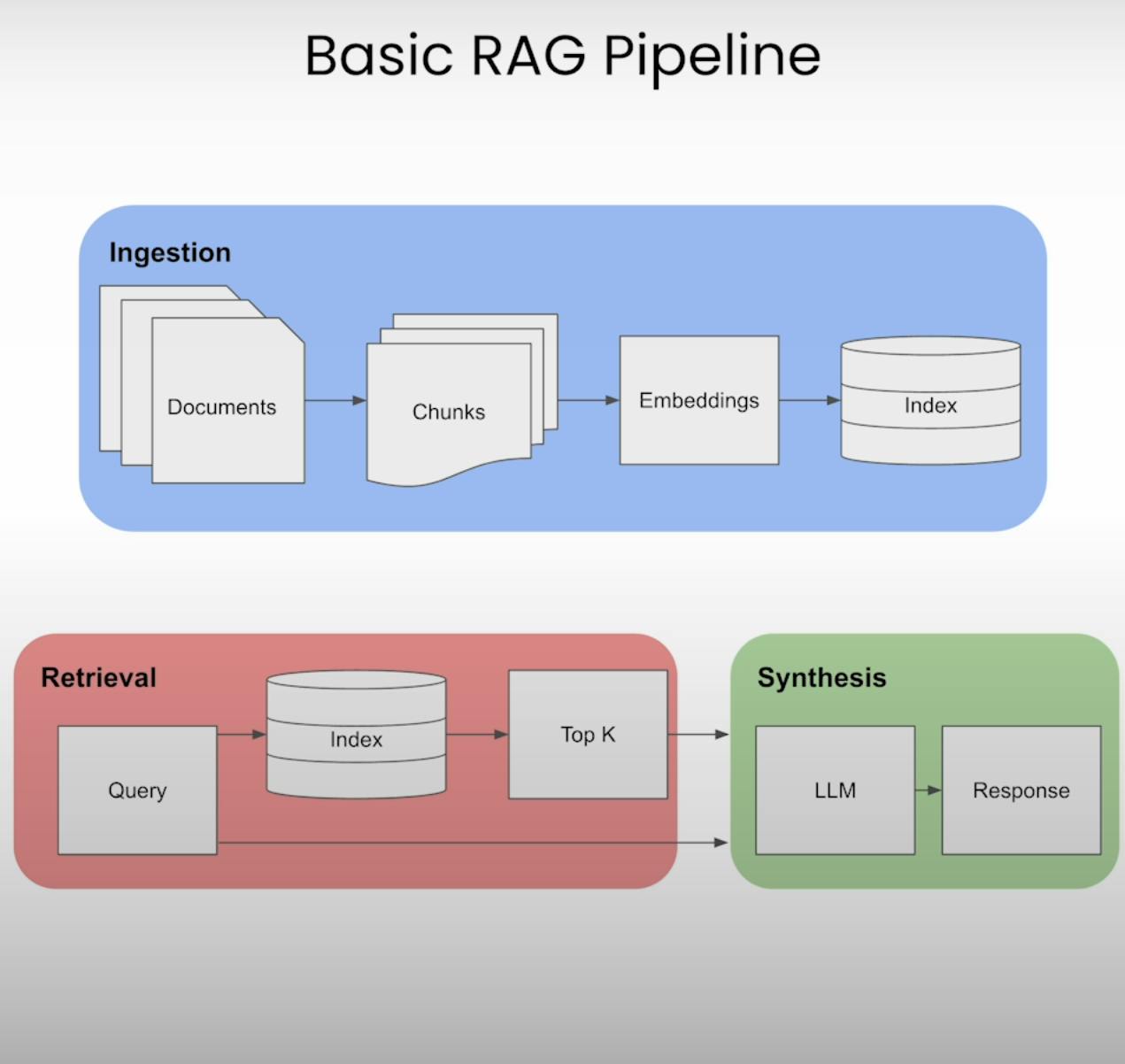
Document Loading and Indexing:
The ebook is parsed and converted into a list of Document objects.
A VectorStoreIndex is created from these documents, enabling similarity-based retrieval.
from llama_index import Document
document = Document(text="\n\n".join([doc.text for doc in documents]))
from llama_index import VectorStoreIndex
from llama_index import ServiceContext
service_context = ServiceContext.from_defaults(
llm=llm, embed_model="local:BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5")
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents([document],
service_context=service_context)
Here, the ebook is converted into a single Document object by joining the text of individual documents with newline characters. Then, a ServiceContext is created with the OpenAI LLM and a specified embedding model. Finally, a VectorStoreIndex is created from the document using the service context, enabling similarity-based retrieval.
Basic RAG Pipeline:
A basic RAG pipeline is implemented using the OpenAI LLM and the VectorStoreIndex.
This pipeline is queried with a question, and the response is printed.
query_engine = index.as_query_engine()
response = query_engine.query(
"What are steps to take when finding projects to build your experience?")
print(str(response))
Output:
Develop a side hustle, ensure the project will help you grow technically, collaborate with good teammates, and consider if the project can be a meaningful stepping stone to larger projects.
Here, a query_engine is obtained from the VectorStoreIndex, allowing querying the index using natural language. The query method is called with a question, and the generated response is printed. This demonstrates a basic RAG pipeline, where relevant information is retrieved from the index and used to generate a final answer using the language model.
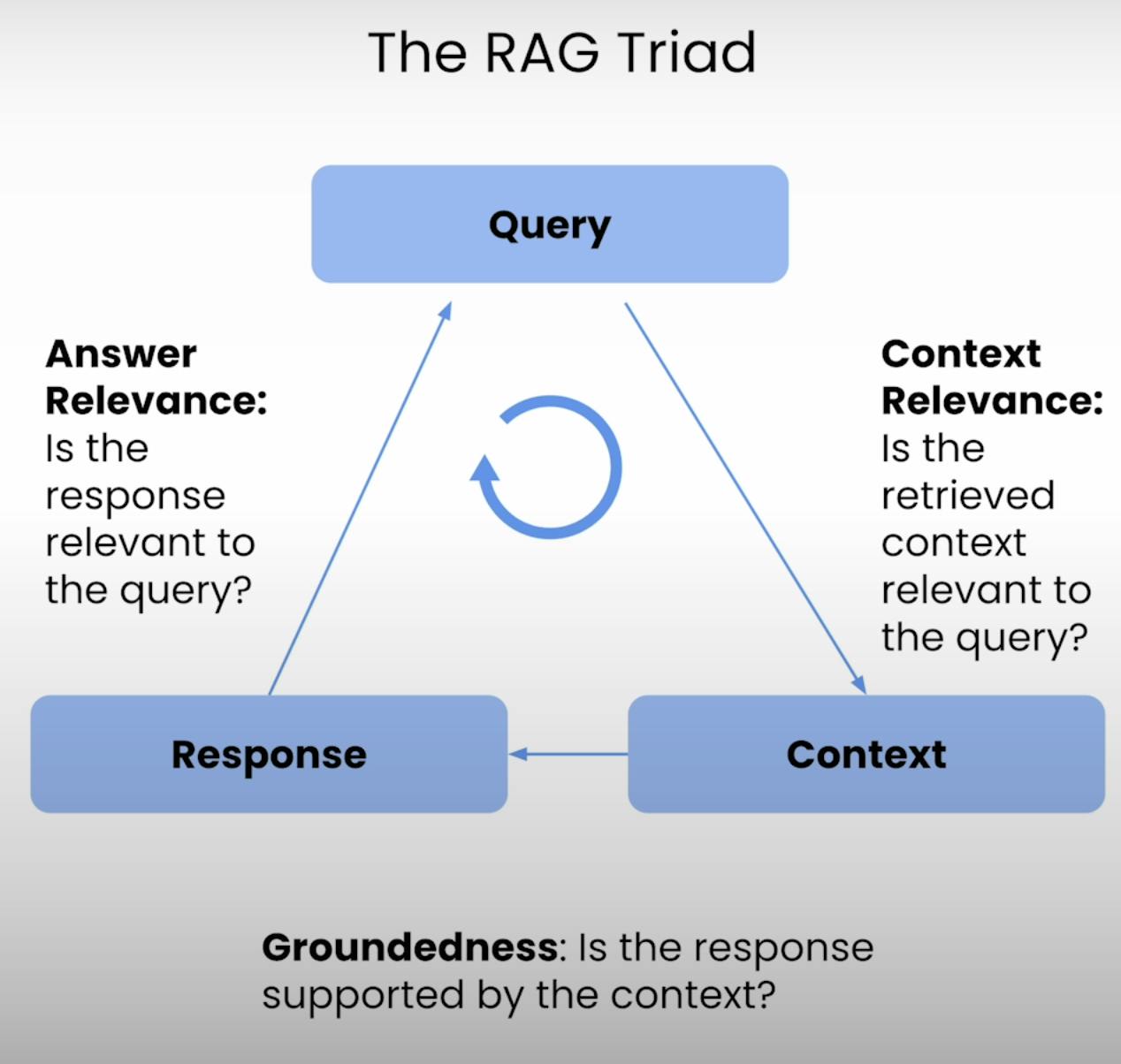
Evaluation Setup with TruLens:
Here TruLens is initialized and configured to record and evaluate the pipeline's performance.
eval_questions = []
with open('eval_questions.txt', 'r') as file:
for line in file:
item = line.strip()
eval_questions.append(item)
from trulens_eval import Tru
tru = Tru()
tru.reset_database()
from utils import get_prebuilt_trulens_recorder
tru_recorder = get_prebuilt_trulens_recorder(query_engine,
app_id="Direct Query Engine")
with tru_recorder as recording:
for question in eval_questions:
response = query_engine.query(question)
First, a list of evaluation questions is loaded from a file eval_questions.txt. Then, the Tru object from TruLens is initialized, and the database is reset. A pre-built TruLens recorder is obtained for the query_engine (the basic RAG pipeline) with a specific app ID. Finally, within the recorder context, each evaluation question is queried through the query_engine, and TruLens records the performance metrics in the background.
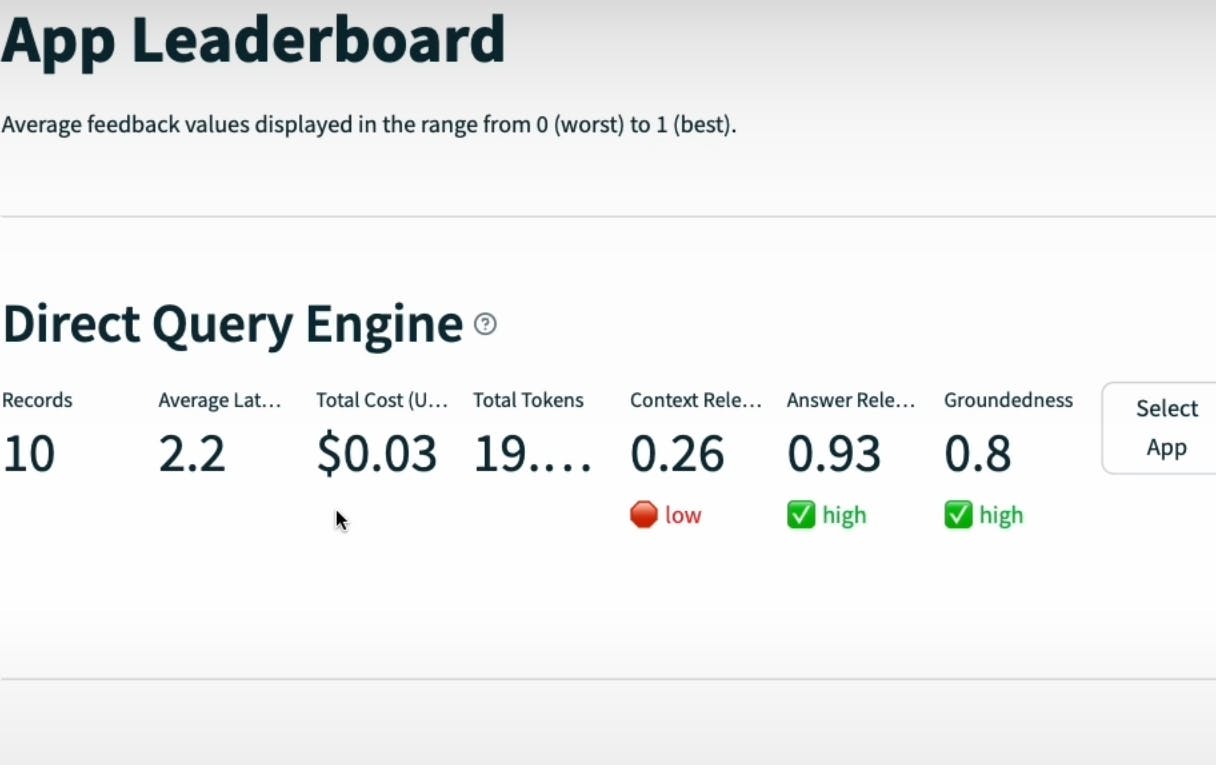
Advanced RAG Pipelines:
Sentence Window Retrieval:

A SentenceWindowIndex is built, focusing on retrieving relevant sentences instead of entire documents.
The pipeline is queried with a question, and the response is evaluated using TruLens.
from llama_index.llms import OpenAI
llm = OpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0.1)
from utils import build_sentence_window_index
sentence_index = build_sentence_window_index(
document,
llm,
embed_model="local:BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5",
save_dir="sentence_index")
from utils import get_sentence_window_query_engine
sentence_window_engine = get_sentence_window_query_engine(sentence_index)
window_response = sentence_window_engine.query(
"how do I get started on a personal project in AI?")
print(str(window_response))
Output:
To get started on a personal project in AI, you can begin by identifying a project that aligns with your career goals and interests. It's important to choose a project that is responsible, ethical, and beneficial to people. Once you have selected a project, you can follow the steps outlined in the chapters provided, such as scoping the project, executing it with an eye toward career development, and building a portfolio that demonstrates skill progression. This approach will help you embark on a meaningful AI project that contributes to your professional growth.
Here, a SentenceWindowIndex is built using a helper function (build_sentence_window_index). This index focuses on retrieving relevant sentences rather than entire documents. A query engine (sentence_window_engine) is then obtained from this index. When a question is queried through this engine, it retrieves relevant sentences and generates a response accordingly.
The performance of this pipeline is evaluated using TruLens, similar to the basic RAG pipeline.
tru.reset_database()
tru_recorder_sentence_window = get_prebuilt_trulens_recorder(
sentence_window_engine,
app_id = "Sentence Window Query Engine")
for question in eval_questions:
with tru_recorder_sentence_window as recording:
response = sentence_window_engine.query(question)
print(question)
print(str(response))
tru.get_leaderboard(app_ids=[])
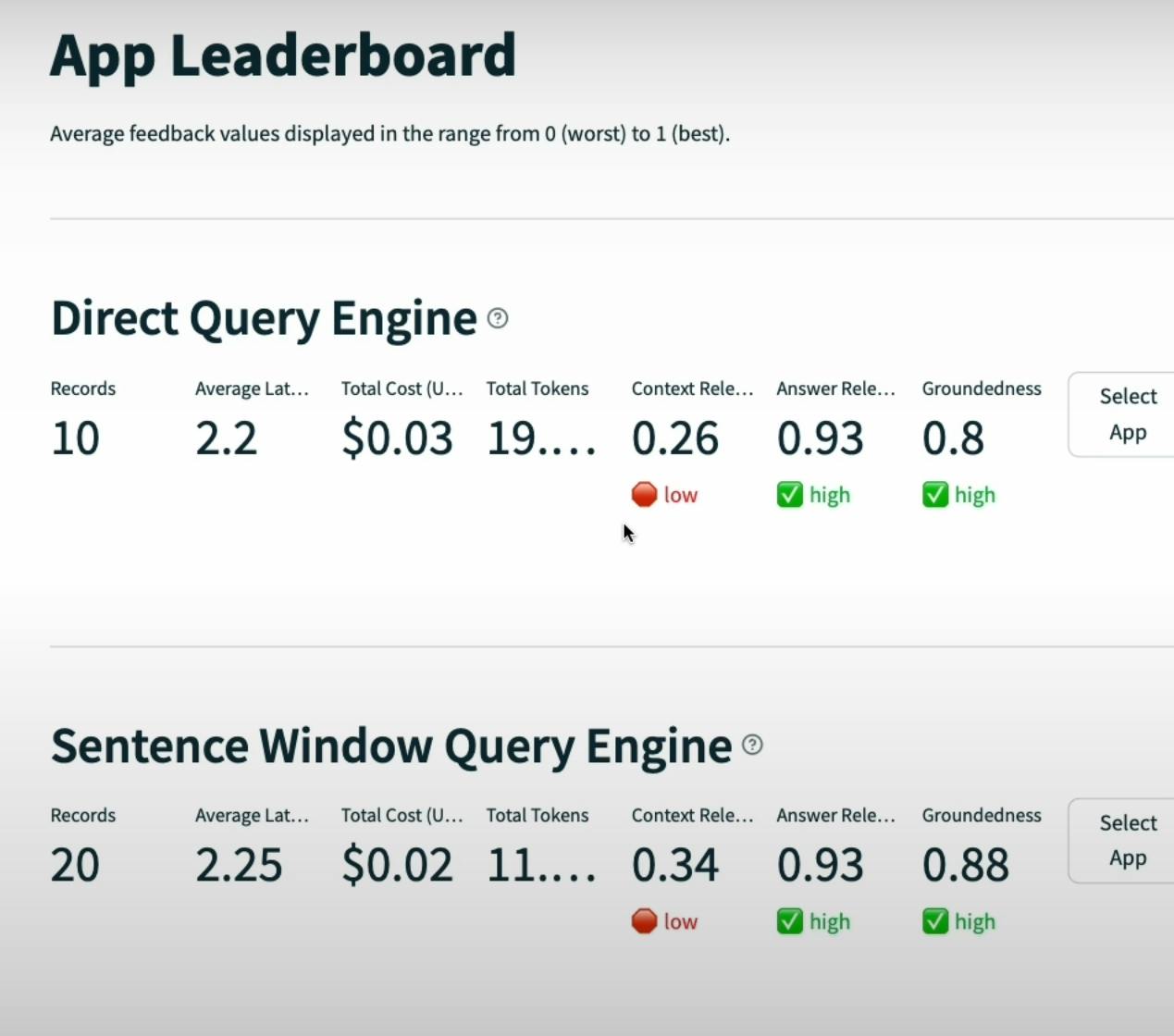
This code resets the TruLens database, creates a new TruLens recorder for the sentence_window_engine, and runs each evaluation question through the engine while recording the performance metrics. Finally, the get_leaderboard function displays the performance metrics for this pipeline.
Auto-merging Retrieval:
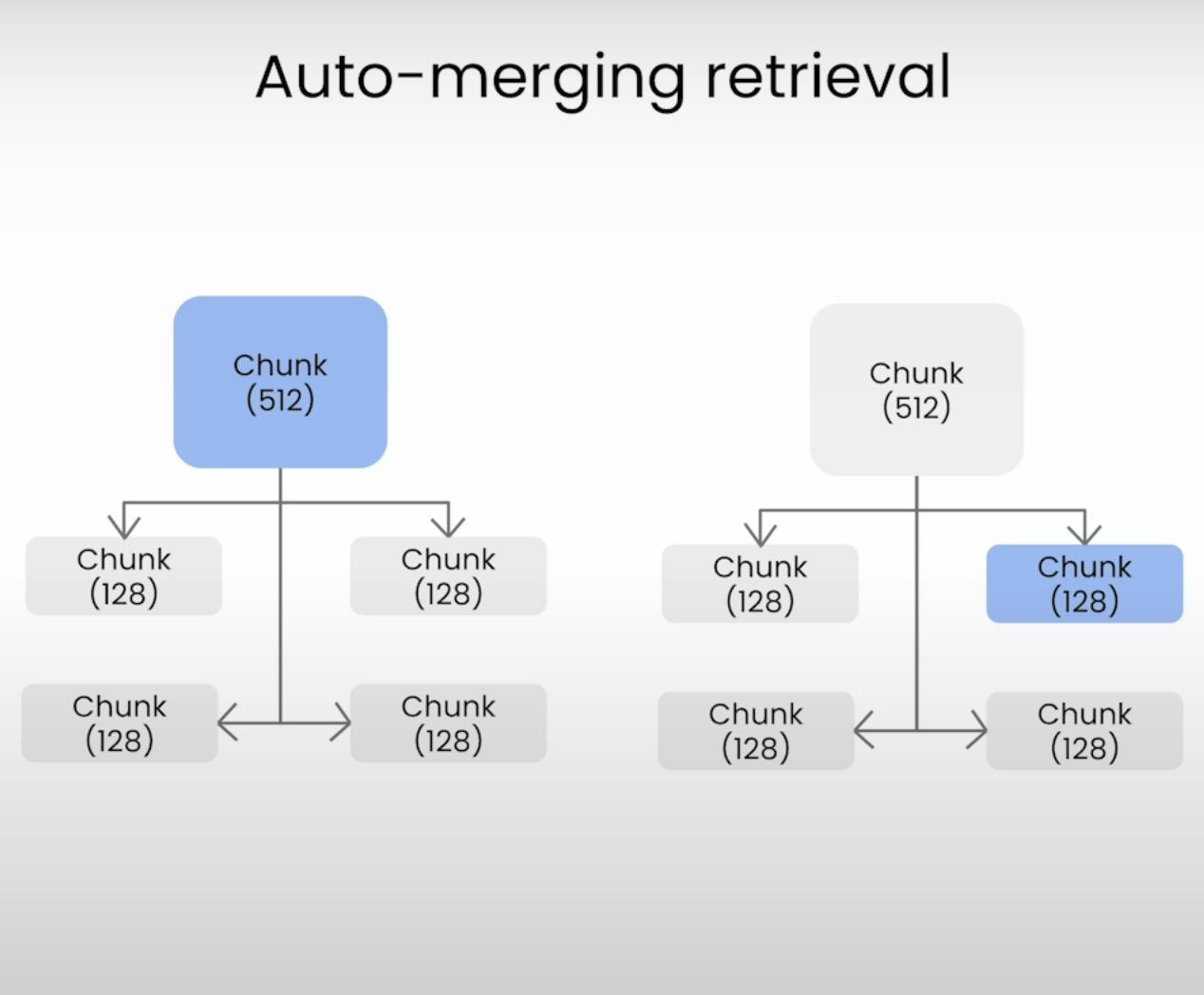
An AutoMergingIndex is created, automatically merging similar nodes in the index for better retrieval.
The pipeline is queried and evaluated similarly to the sentence window approach.
from utils import build_automerging_index
automerging_index = build_automerging_index(
documents,
llm,
embed_model="local:BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5",
save_dir="merging_index")
from utils import get_automerging_query_engine
automerging_query_engine = get_automerging_query_engine(
automerging_index)
auto_merging_response = automerging_query_engine.query(
"How do I build a portfolio of AI projects?")
print(str(auto_merging_response))
Output:
Building a portfolio of AI projects involves showcasing a progression from simple to complex undertakings over time. It is important to be able to effectively communicate your thinking to demonstrate the value of your work and gain the trust of others. Additionally, identifying ideas that are worth working on is a crucial skill for an AI architect. By working on projects across various industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, climate change, agriculture, ecommerce, and advertising, you can gain valuable experience and build a diverse portfolio.
In this code, an AutoMergingIndex is built using a helper function (build_automerging_index). This index automatically merges similar nodes, aiming to improve retrieval performance. A query engine (automerging_query_engine) is obtained from this index, and a sample question is queried to demonstrate its behavior.
Similar to the sentence window approach, the auto-merging retrieval pipeline is evaluated using TruLens:
tru.reset_database()
tru_recorder_automerging = get_prebuilt_trulens_recorder(automerging_query_engine,
app_id="Automerging Query Engine")
for question in eval_questions:
with tru_recorder_automerging as recording:
response = automerging_query_engine.query(question)
print(question)
print(response)
tru.get_leaderboard(app_ids=[])
The database is reset, a new TruLens recorder is created for the automerging_query_engine, and each evaluation question is queried while recording performance metrics. Finally, the leaderboard is displayed, showing the performance of this pipeline compared to others.

Performance Comparison:
TruLens leaderboard is used to compare the performance of different RAG pipelines based on metrics like answer relevance, context relevance, groundedness, latency, and cost.
Launching TruLens Dashboard
tru.run_dashboard()
This launches the TruLens dashboard, which provides a user interface to interact with the evaluation results. The dashboard allows you to view the performance metrics, inspect individual records, and explore the data in various ways.
Output:
Starting dashboard ...
Config file already exists. Skipping writing process.
Credentials file already exists. Skipping writing process.
Dashboard already running at path: https://s172-31-14-245p18021.lab-aws-production.deeplearning.ai/
If the dashboard is already running, it will provide the URL where the dashboard is hosted.
# Stop the dashboard
tru.stop_dashboard()
This will stop the currently running TruLens dashboard.
The TruLens dashboard is a useful tool for analyzing and visualizing the evaluation results, making it easier to understand the performance of your models and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion:
Evaluating the performance of natural language processing systems is important for understanding their strengths and weaknesses, and for identifying areas for improvement. In this blog post, I demonstrated how to set up and evaluate Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines using LlamaIndex and TruLens. By using LlamaIndex's document indexing capabilities and TruLens's evaluation metrics, and compare the performance of different retrieval techniques, such as sentence window retrieval and auto-merging retrieval, against a baseline RAG pipeline.

