Have you ever wished you could engage in a seamless conversation with your data? Imagine having a virtual assistant that can understand your questions, retrieve relevant information from documents, and provide thoughtful, contextual responses. You can create this by using Language Models and LangChain.
In this blog post, I'll guide you to create a conversational chatbot that can answer questions based on your documents.

Loading and Preparing Data:
First we need to ensure that data is properly loaded and prepared. LangChain offers a variety of document loaders, allowing you to use info from various sources, such as PDFs, Word documents, and even websites.
from langchain.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
loader = PyPDFLoader('path/to/your/file.pdf')
documents = loader.load()
Once we've loaded our documents, we need to split them into manageable chunks. This process is crucial for efficient retrieval and processing. LangChain provides several text splitters, including the CharacterTextSplitter and the RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter, which can intelligently split documents based on specified criteria.
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=150)
docs = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
Now that our documents are loaded and split, we need to create embeddings and a vector store. Embeddings are numerical representations of text that capture semantic meaning, enabling efficient similarity searches. LangChain supports various embedding models, including OpenAI's embeddings.
from langchain.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
vectordb = Chroma.from_documents(docs, embeddings)
With our data loaded, split, and embedded, we're ready to move on to the next phase: retrieval and answer generation.
Advanced Retrieval Techniques:
Retrieving relevant information from our vector store is an important step in answering questions effectively. LangChain offers several retrieval methods, including similarity search, which retrieves documents based on their semantic similarity to the query.
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
query = "What are the major topics covered in this course?"
relevant_docs = vectordb.similarity_search(query, k=3)
However, similarity search is just the beginning. LangChain provides advanced retrieval algorithms that can overcome edge cases and improve the quality of retrieved results. Techniques like self-query, compression, and more can be leveraged to enhance the retrieval process.
Combining Retrieval with Language Models:
Now that we have our relevant documents, it's time to integrate them with Language Models for answer generation. LangChain makes this process easier by providing a RetrievalQA chain that combines document retrieval and Language Model querying.
# Build prompt
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
template = """Use the following pieces of context to answer the question
at the end. If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know,
don't try to make up an answer. Use three sentences maximum.
Keep the answer as concise as possible. Always say "thanks for asking!"
at the end of the answer.
{context}
Question: {question}
Helpful Answer:"""
QA_CHAIN_PROMPT = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["context", "question"],
template=template,)
# Run chain
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
question = "Is probability a class topic?"
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm,
retriever=vectordb.as_retriever(),
return_source_documents=True,
chain_type_kwargs={"prompt": QA_CHAIN_PROMPT})
result = qa_chain({"query": question})
result["result"]
# Output: 'Yes, probability is a class topic as the instructor assumes
# familiarity with basic probability and statistics. Thanks for asking!'
With this setup, our chatbot can retrieve relevant documents and use the Language Model to generate a concise and coherent answer to the user's query.
Creating a Conversational Chatbot:
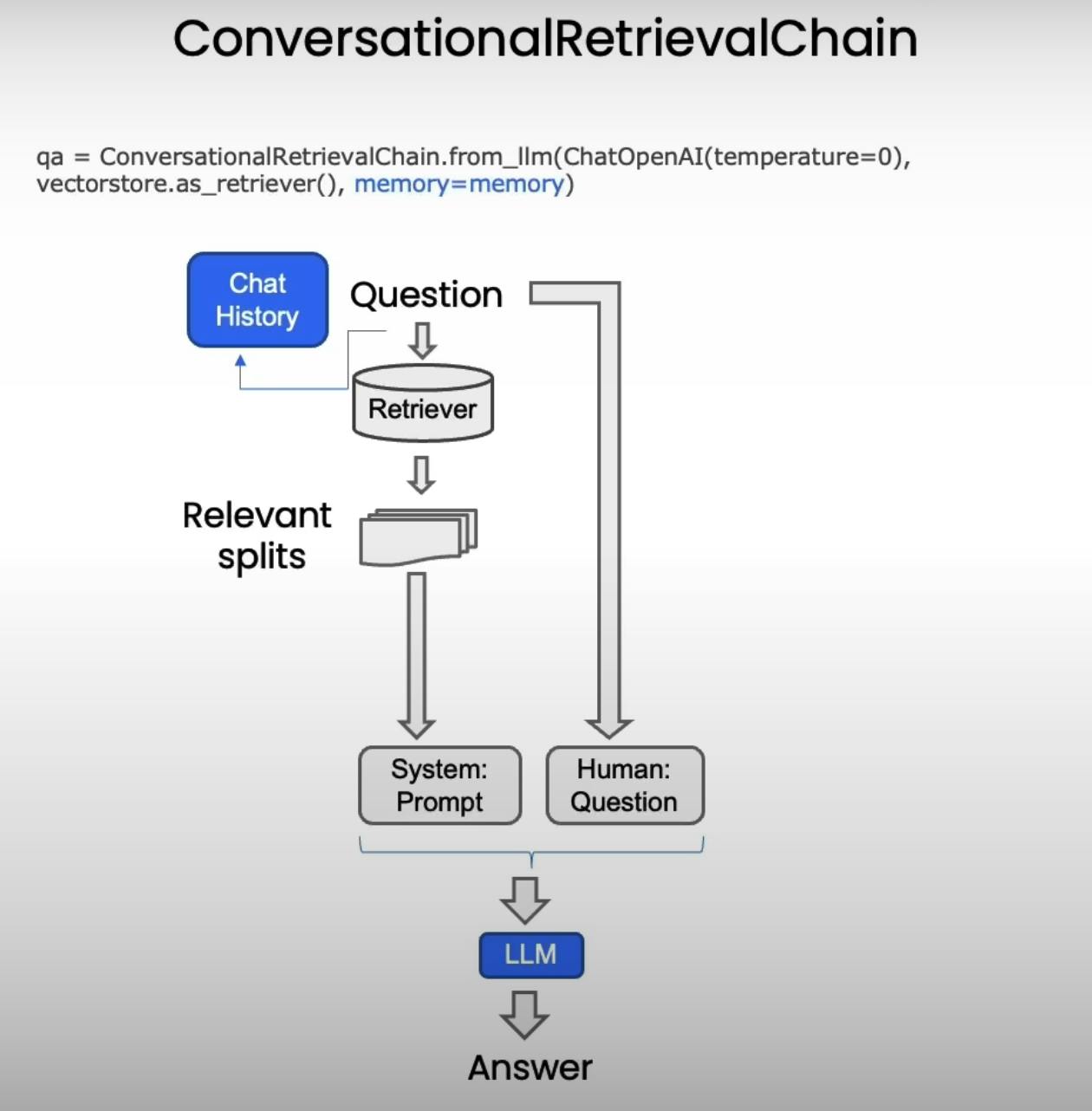

While our current setup allows us to answer individual questions, true conversational capabilities require handling follow-up questions and maintaining context. This is where LangChain's memory management comes into play.
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain.chains import ConversationalRetrievalChain
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="chat_history",
return_messages=True)
retriever=vectordb.as_retriever()
qa = ConversationalRetrievalChain.from_llm(
llm,
retriever=retriever,
memory=memory
)
By incorporating ConversationBufferMemory and using the ConversationalRetrievalChain, our chatbot can now maintain a history of the conversation and provide contextual responses to follow-up questions.
question = "Is probability a class topic?"
result = qa({"question": question})
The chatbot can now refer to the previous conversation and provide a relevant response to the follow-up question, creating a more natural and engaging experience.
Create a chatbot that works on your documents
While our chatbot is functional, a user-friendly interface can significantly enhance the overall experience. LangChain provides an easy way to create a graphical user interface (GUI) for our chatbot, complete with tabs for conversation, database, chat history, and configuration.
from langchain.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.text_splitter import CharacterTextSplitter, RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.vectorstores import DocArrayInMemorySearch
from langchain.document_loaders import TextLoader
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA, ConversationalRetrievalChain
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.document_loaders import TextLoader
from langchain.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
def load_db(file, chain_type, k):
# load documents
loader = PyPDFLoader(file)
documents = loader.load()
# split documents
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=150)
docs = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
# define embedding
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
# create vector database from data
db = DocArrayInMemorySearch.from_documents(docs, embeddings)
# define retriever
retriever = db.as_retriever(search_type="similarity", search_kwargs={"k": k})
# create a chatbot chain. Memory is managed externally.
qa = ConversationalRetrievalChain.from_llm(
llm=ChatOpenAI(model_name=llm_name, temperature=0),
chain_type=chain_type,
retriever=retriever,
return_source_documents=True,
return_generated_question=True,
)
return qa
import panel as pn
import param
class cbfs(param.Parameterized):
chat_history = param.List([])
answer = param.String("")
db_query = param.String("")
db_response = param.List([])
def __init__(self, **params):
super(cbfs, self).__init__( **params)
self.panels = []
self.loaded_file = "docs/cs229_lectures/MachineLearning-Lecture01.pdf"
self.qa = load_db(self.loaded_file,"stuff", 4)
def call_load_db(self, count):
if count == 0 or file_input.value is None: # init or no file specified :
return pn.pane.Markdown(f"Loaded File: {self.loaded_file}")
else:
file_input.save("temp.pdf") # local copy
self.loaded_file = file_input.filename
button_load.button_style="outline"
self.qa = load_db("temp.pdf", "stuff", 4)
button_load.button_style="solid"
self.clr_history()
return pn.pane.Markdown(f"Loaded File: {self.loaded_file}")
def convchain(self, query):
if not query:
return pn.WidgetBox(pn.Row('User:', pn.pane.Markdown("", width=600)), scroll=True)
result = self.qa({"question": query, "chat_history": self.chat_history})
self.chat_history.extend([(query, result["answer"])])
self.db_query = result["generated_question"]
self.db_response = result["source_documents"]
self.answer = result['answer']
self.panels.extend([
pn.Row('User:', pn.pane.Markdown(query, width=600)),
pn.Row('ChatBot:', pn.pane.Markdown(self.answer, width=600, style={'background-color': '#F6F6F6'}))
])
inp.value = '' #clears loading indicator when cleared
return pn.WidgetBox(*self.panels,scroll=True)
@param.depends('db_query ', )
def get_lquest(self):
if not self.db_query :
return pn.Column(
pn.Row(pn.pane.Markdown(f"Last question to DB:", styles={'background-color': '#F6F6F6'})),
pn.Row(pn.pane.Str("no DB accesses so far"))
)
return pn.Column(
pn.Row(pn.pane.Markdown(f"DB query:", styles={'background-color': '#F6F6F6'})),
pn.pane.Str(self.db_query )
)
@param.depends('db_response', )
def get_sources(self):
if not self.db_response:
return
rlist=[pn.Row(pn.pane.Markdown(f"Result of DB lookup:", styles={'background-color': '#F6F6F6'}))]
for doc in self.db_response:
rlist.append(pn.Row(pn.pane.Str(doc)))
return pn.WidgetBox(*rlist, width=600, scroll=True)
@param.depends('convchain', 'clr_history')
def get_chats(self):
if not self.chat_history:
return pn.WidgetBox(pn.Row(pn.pane.Str("No History Yet")), width=600, scroll=True)
rlist=[pn.Row(pn.pane.Markdown(f"Current Chat History variable", styles={'background-color': '#F6F6F6'}))]
for exchange in self.chat_history:
rlist.append(pn.Row(pn.pane.Str(exchange)))
return pn.WidgetBox(*rlist, width=600, scroll=True)
def clr_history(self,count=0):
self.chat_history = []
return
cb = cbfs()
file_input = pn.widgets.FileInput(accept='.pdf')
button_load = pn.widgets.Button(name="Load DB", button_type='primary')
button_clearhistory = pn.widgets.Button(name="Clear History", button_type='warning')
button_clearhistory.on_click(cb.clr_history)
inp = pn.widgets.TextInput( placeholder='Enter text here…')
bound_button_load = pn.bind(cb.call_load_db, button_load.param.clicks)
conversation = pn.bind(cb.convchain, inp)
jpg_pane = pn.pane.Image( './img/convchain.jpg')
tab1 = pn.Column(
pn.Row(inp),
pn.layout.Divider(),
pn.panel(conversation, loading_indicator=True, height=300),
pn.layout.Divider(),
)
tab2= pn.Column(
pn.panel(cb.get_lquest),
pn.layout.Divider(),
pn.panel(cb.get_sources ),
)
tab3= pn.Column(
pn.panel(cb.get_chats),
pn.layout.Divider(),
)
tab4=pn.Column(
pn.Row( file_input, button_load, bound_button_load),
pn.Row( button_clearhistory, pn.pane.Markdown("Clears chat history. Can use to start a new topic" )),
pn.layout.Divider(),
pn.Row(jpg_pane.clone(width=400))
)
dashboard = pn.Column(
pn.Row(pn.pane.Markdown('# ChatWithYourData_Bot')),
pn.Tabs(('Conversation', tab1), ('Database', tab2), ('Chat History', tab3),('Configure', tab4))
)
dashboard

With this intuitive interface, users can easily upload their documents, configure settings, view the conversation history, and interact with the chatbot in a seamless manner.
Conclusion:
By incorporating memory management and the ConversationalRetrievalChain, our chatbot gained the ability to understand and respond to follow-up questions, creating a more natural and engaging conversational experience.
Finally, we wrapped our chatbot in a user-friendly interface, making it accessible and intuitive for users to interact with their data.

